QUALITY ASSURANCE
Quality Assurance (QA) is an essential element of any research and demonstrates a commitment by management and researchers to ensure the reliability of results and data generated, and provide confidence in the research undertaken.
Highlights of QA Team at KlinEra:
- Huge QA Team with Wide variety of Experience.
- 100 % Trial Data Verification for compliance check with Protocol, SOP, GCP and applicable regulatory requirements.
- In-still the importance of quality in everything we do as an organisation.
- We encourage and are open to have constructive feedback.
- Embed QA into systems and methods.
- Have a written quality-management system.
- Document all internal processes.
- Have a dedicated client team to gather feedback.
- Set the right expectations for tasks and handling issues.
We Assure Quality by Sponsor Monitoring, Self-monitoring, Self-checks, Written procedures.
Ask monitor to send the written Monitoring report to verify findings.
Use report as a to-do list Write on report as you resolve things Consider the IRB’s reporting requirements Review with PI; PI should sign if possible
Use report as a to-do list Write on report as you resolve things Consider the IRB’s reporting requirements Review with PI; PI should sign if possible
Responding to monitoring findings
If findings are wrong, we provide documentation to monitor and ask for a revised letter.
If findings are wrong, we provide documentation to monitor and ask for a revised letter.
Problems in Research Steps to resolve problems Identify problems
Make immediate corrections, Evaluate risk, Identify root cause of each problem, Identify corrective and preventive action for each root cause.
Make immediate corrections, Evaluate risk, Identify root cause of each problem, Identify corrective and preventive action for each root cause.
Corrections “Immediate corrections” include
Evaluating rights, welfare, and safety of subject Reporting, if applicable: subject, subject’s family, sponsor, and/or IRB
Evaluating rights, welfare, and safety of subject Reporting, if applicable: subject, subject’s family, sponsor, and/or IRB
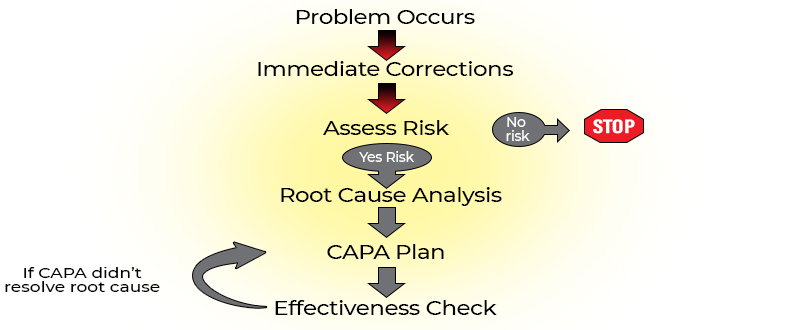
The root cause is the initiating, most basic cause of a problem that may or may not lead to a chain of causes or other problems. Eliminating the root cause should prevent recurrence of the problem
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The RCA is the process of identifying the root cause and the downstream effect on the causal chain Since non-compliance is usually from a system failure, not a person failure, RCA should focus on identifying underlying problems that contribute to error rather than focusing on mistakes made by individuals
The RCA is the process of identifying the root cause and the downstream effect on the causal chain Since non-compliance is usually from a system failure, not a person failure, RCA should focus on identifying underlying problems that contribute to error rather than focusing on mistakes made by individuals
What is CAPA? Corrective and Preventive Actions
Corrective Actions
The process of reacting to an existing problem and fixing it
The process of reacting to an existing problem and fixing it
Preventive Actions
The process of detecting potential problems and eliminating them
The process of detecting potential problems and eliminating them
CAPA Don’ts! We will retrain the study team…
Study team members have been terminated or will be reassigned…We will have 5 people check….
Study team members have been terminated or will be reassigned…We will have 5 people check….
CAPA Musts!
Corrective: Assess and correct safety/rights/welfare of subjects. Report to subjects, IRB, sponsor, and/or internal department. Document corrections.
Preventive: Develop and document a process, train on the process, implement the process, evaluate the process, amend process as necessary.
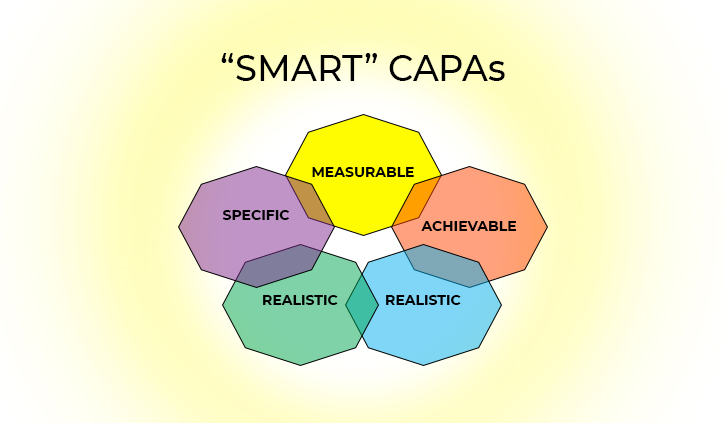
“SMART” CAPAs
Effectiveness Check Build in an effectiveness check as the final step of CAPA Effectiveness checks verify that the CAPAs resolved the root cause.
Documenting the CAPA Action type (corrective or preventive)
Action description Owner Due date Plan for effectiveness check Effectiveness check outcome
Action description Owner Due date Plan for effectiveness check Effectiveness check outcome

In Summary Problem occurs Immediate corrections taken
Determine impact of problem and risk of recurrence (risk = severity + frequency)Root cause analysis CAPA plan Effectiveness check
Determine impact of problem and risk of recurrence (risk = severity + frequency)Root cause analysis CAPA plan Effectiveness check
Quality checks is applied at each stage of data handling to ensure that all the date are reliable and have been processed correctly.
We have quality review metrics with defined role in the QA Team as per the project requirements.
Periodic internal Process Audits/Annual Audit plans.

